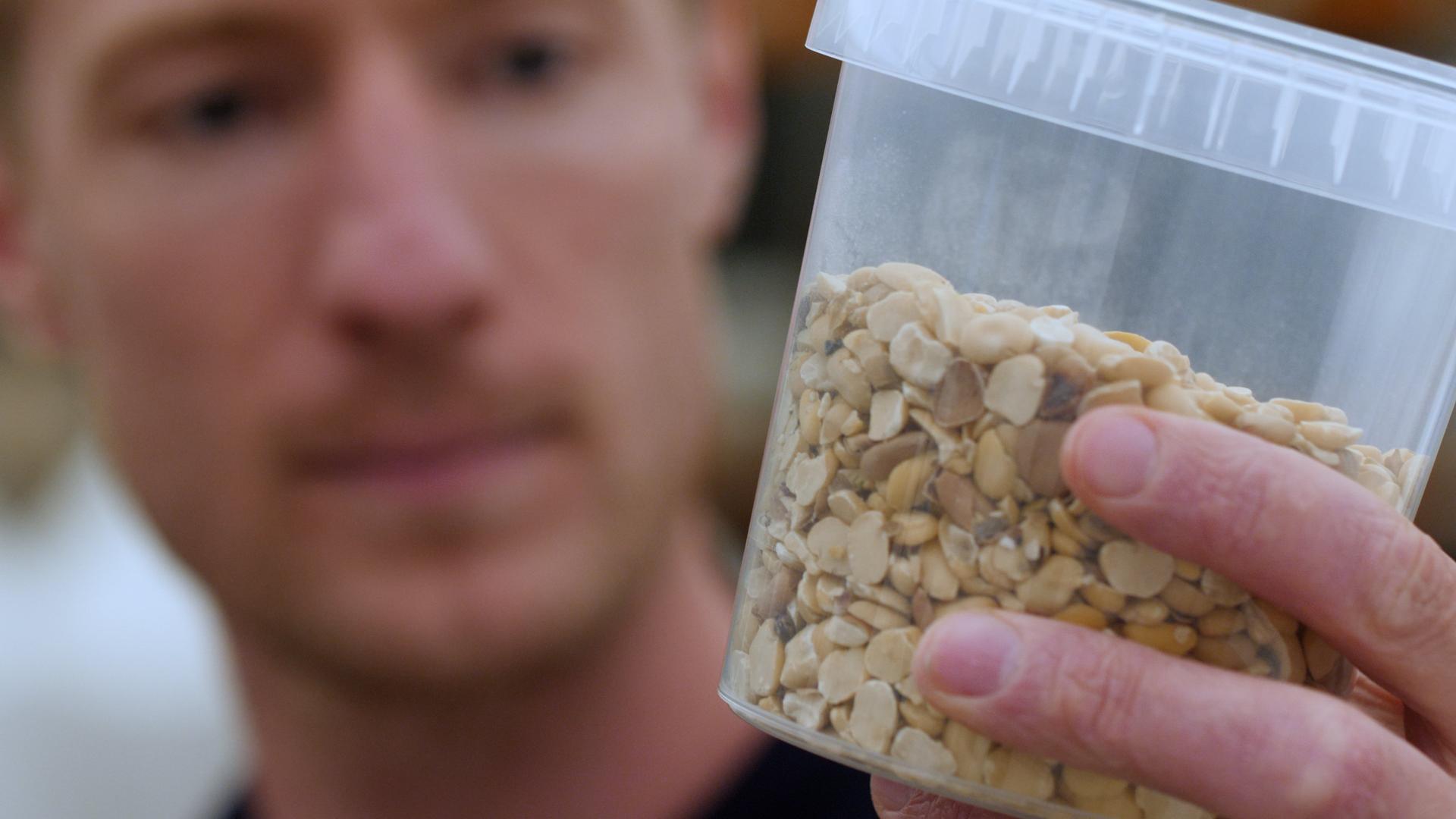
Changing feed formulas can be challenging, as new materials must meet stringent requirements to maintain growth, feed conversion rates, robustness, health, and welfare. Fishmeal, for example, is highly stable and rich in digestible protein and essential amino acids, making it an important part of the diet. Successful replacement of fishmeal with plant-based proteins requires careful nutrient supplementation, such as amino acids, to avoid growth and welfare issues.
Marine oils, another key component, supply essential omega-3 fatty acids like EPA and DHA, which are critical for maintaining robustness and immune health under modern farming conditions. Replacing these oils with alternatives requires careful supplementation of fat-soluble vitamins. BioMar’s R&D team has gained extensive knowledge in transitioning from marine ingredients to processed animal products, plant-based proteins, and more recently, novel sources.